Introduction of Programming Paradigms(编程范式简介)
A paradigm can also be termed as a method to solve a problem or accomplish a task. A programming paradigm is an approach to solving a problem using a specific programming language. In other words, it is a methodology for problem-solving using the tools and techniques available to us, following a particular approach. While there are many programming languages, each of them typically adheres to one or more paradigms that guide how the language is implemented.
范式也可以被称为解决问题或完成任务的方法。编程范式是一种使用特定编程语言解决问题的方法。换句话说,它是利用我们可用的工具和技术,按照特定方法解决问题的一种方法论。尽管有许多编程语言,但每种语言通常都遵循一种或多种范式来指导语言的实现。
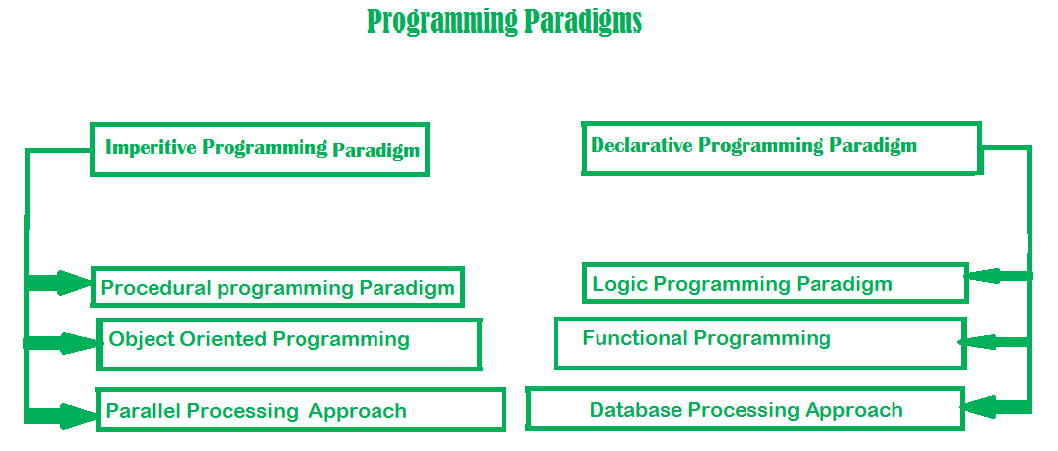
These methodologies or strategies are referred to as programming paradigms. Apart from the variety of programming languages available, there are several paradigms that address different demands and challenges in software development. These paradigms are discussed below:
这些方法论或策略被称为编程范式。除了各种编程语言之外,还有几种范式可以解决软件开发中的不同需求和挑战。这些范式如下所述:
Imperative programming paradigm(命令式编程范式)
It is one of the oldest programming paradigm. It features close relation to machine architecture. It is based on Von Neumann architecture. It works by changing the program state through assignment statements. It performs step by step task by changing state. The main focus is on how to achieve the goal. The paradigm consist of several statements and after execution of all the result is stored.
命令式编程范式是最古老的编程范式之一。它与计算机架构关系密切,基于冯·诺依曼架构。它通过赋值语句改变程序状态来工作,通过逐步改变状态来完成任务。其主要关注点是如何实现目标。该范式由多个语句组成,所有语句执行完毕后将结果存储起来。
Advantages:
- Very simple to implement 实现非常简单
- It contains loops, variables etc. 包含循环、变量等
Disadvantage:
- Complex problem cannot be solved 无法解决复杂问题
- Less efficient and less productive 效率较低,生产力不高
- Parallel programming is not possible 不支持并行编程
Examples of Imperative programming paradigm:
C:developed by Dennis Ritchie and Ken Thompson
Fortran:developed by John Backus for IBM
Basic:developed by John G Kemeny and Thomas E Kurtz
命令式编程范式的示例:
C:由丹尼斯·里奇(Dennis Ritchie)和肯·汤普森(Ken Thompson)开发
Fortran:由约翰·巴库斯(John Backus)为 IBM 开发
Basic:由约翰·G·基门尼(John G. Kemeny)和托马斯·E·库尔茨(Thomas E. Kurtz)开发
C++
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// Array to store marks
int marks[5] = { 12, 32, 45, 13, 19 };
// Variable to store the sum of marks
int sum = 0;
// Variable to store the average
float average = 0.0;
// Calculate the sum of marks
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum = sum + marks[i];
}
// Calculate the average
average = sum / 5.0;
// Output the average
std::cout << "Average of five numbers: " << average << std::endl;
return 0;
}
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// Array to store marks
int marks[5] = { 12, 32, 45, 13, 19 };
// Variable to store the sum of marks
int sum = 0;
// Variable to store the average
float average = 0.0;
// Calculate the sum of marks
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum = sum + marks[i];
}
// Calculate the average
average = (float)sum / 5.0;
// Output the average
printf("Average of five numbers: %.2f\n", average);
return 0;
}
Java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Array to store marks
int[] marks = {12, 32, 45, 13, 19};
// Variable to store the sum of marks
int sum = 0;
// Variable to store the average
float average = 0.0f;
// Calculate the sum of marks
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum = sum + marks[i];
}
// Calculate the average
average = sum / 5.0f;
// Output the average
System.out.println("Average of five numbers: " + average);
}
}
Python
def main():
# Array to store marks
marks = [12, 32, 45, 13, 19]
# Variable to store the sum of marks
total_marks = sum(marks)
# Calculate the average
average = total_marks / len(marks)
# Output the average
print("Average of five numbers:", average)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
#this code is added by Utkarsh
JavaScript
// Array to store marks
let marks = [12, 32, 45, 13, 19];
// Variable to store the sum of marks
let sum = 0;
// Variable to store the average
let average = 0.0;
// Calculate the sum of marks
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum = sum + marks[i];
}
// Calculate the average
average = sum / 5.0;
// Output the average
console.log("Average of five numbers: " + average);
Output
Average of five numbers: 24.2
Imperative programming is divided into three broad categories: Procedural, OOP and parallel processing. These paradigms are as follows:
命令式编程分为三大类:过程式、面向对象和并行处理。这些范式如下所述:
Procedural programming paradigm(过程式编程范式)
This paradigm emphasizes on procedure in terms of under lying machine model. There is no difference in between procedural and imperative approach. It has the ability to reuse the code and it was boon at that time when it was in use because of its reusability.
该范式强调过程,即底层机器模型。过程式编程与命令式编程没有区别。它能够重用代码,当时它被使用时,由于其可重用性,它是一个巨大的优势。
Examples of Procedural programming paradigm:
C:developed by Dennis Ritchie and Ken Thompson
C++:developed by Bjarne Stroustrup
Java:developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems
ColdFusion:developed by J J Allaire
Pascal:developed by Niklaus Wirth
过程式编程范式的示例:
C:由丹尼斯·里奇(Dennis Ritchie)和肯·汤普森(Ken Thompson)开发
C++:由比雅尼·斯特劳斯特鲁普(Bjarne Stroustrup)开发
Java:由詹姆斯·高斯林(James Gosling)在Sun Microsystems开发
ColdFusion:由J. J. Allaire开发
Pascal:由尼克劳斯·维尔特(Niklaus Wirth)开发
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i, fact = 1, num;
cout << "Enter any Number: ";
cin >> number;
for (i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact = fact * i;
}
cout << "Factorial of " << num << " is: " << fact << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Scanner object for reading input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Prompt user to enter a number
System.out.println("Enter any Number: ");
// Read number from user input
int num = scanner.nextInt();
// Initialize factorial to 1
int fact = 1;
// Calculate factorial using a for loop
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact = fact * i;
}
// Print the factorial of the number
System.out.println("Factorial of " + num + " is: " + fact);
}
}
Python
# Prompt user to enter a number
num = int(input("Enter any Number: "))
fact = 1 # Initialize factorial variable
# Calculate factorial
for i in range(1, num + 1):
fact = fact * i
# Print the factorial
print("Factorial of", num, "is:", fact)
Javascript
// Prompt the user for input
let num = prompt("Enter any Number: ");
// Initialize the factorial value to 1
let fact = 1;
// Calculate the factorial of the number
for (let i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact = fact * i;
}
// Print the factorial of the number
console.log("Factorial of " + num + " is: " + fact);
Object oriented programming(面向对象编程范式)
The program is written as a collection of classes and object which are meant for communication. The smallest and basic entity is object and all kind of computation is performed on the objects only. More emphasis is on data rather procedure. It can handle almost all kind of real life problems which are today in scenario.
程序被编写成一系列类和对象的集合,这些类和对象用于通信。最基本的实体是对象,所有计算都在对象上进行。更强调数据而不是过程。它可以处理几乎所有当前场景中的现实问题。
Advantages:
- Data security 数据安全性
- Inheritance 继承
- Code reusability 代码可重用性
- Flexible and abstraction is also present 灵活且具有抽象性
Examples of Object Oriented programming paradigm:
Simula:first OOP language
Java:developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems
C++:developed by Bjarne Stroustrup
Objective-C:designed by Brad Cox
Visual Basic .NET:developed by Microsoft
Python:developed by Guido van Rossum
Ruby:developed by Yukihiro Matsumoto
Smalltalk:developed by Alan Kay, Dan Ingalls, Adele Goldberg
面向对象编程范式的示例:
Simula:第一种面向对象的编程语言
Java:由詹姆斯·高斯林(James Gosling)在Sun Microsystems开发
C++:由比雅尼·斯特劳斯特鲁普(Bjarne Stroustrup)开发
Objective-C:由布拉德·考克斯(Brad Cox)设计
Visual Basic .NET:由微软开发
Python:由吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum)开发
Ruby:由松本行弘(Yukihiro Matsumoto)开发
Smalltalk:由艾伦·凯(Alan Kay)、丹·英格尔斯(Dan Ingalls)和阿德莱·戈德堡(Adele Goldberg)开发
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Class Signup
class Signup {
int userid;
string name;
string emailid;
char sex;
long mob;
public:
// Function to create and object using
// the parameters
void create(int userid, string name, string emailid,
char sex, long mob)
{
cout << "Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create "
"your account\n";
this->userid = 132;
this->name = "Radha";
this->emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com";
this->sex = 'F';
this->mob = 900558981;
cout << "your account has been created" << endl;
}
};
// Driver Cpde
int main()
{
cout << "GfG!" << endl;
// Creating Objects
Signup s1;
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F', 89002);
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("GfG!");
Signup s1 = new Signup();
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F',
89002);
}
}
class Signup {
int userid;
String name;
String emailid;
char sex;
long mob;
public void create(int userid, String name,
String emailid, char sex, long mob)
{
System.out.println(
"Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create your account\n");
this.userid = 132;
this.name = "Radha";
this.emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com";
this.sex = 'F';
this.mob = 900558981;
System.out.println("your account has been created");
}
}
Python
class Signup:
def __init__(self):
self.userid = 0
self.name = ""
self.emailid = ""
self.sex = ""
self.mob = 0
def create(self, userid, name, emailid, sex, mob):
print("Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create your account\n")
self.userid = 132
self.name = "Radha"
self.emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com"
self.sex = 'F'
self.mob = 900558981
print("your account has been created")
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("GfG!")
s1 = Signup()
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F', 89002)
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("GfG!");
Signup s1 = new Signup();
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F',
89002);
}
}
class Signup {
public int userid;
public string name;
public string emailid;
public char sex;
public long mob;
public void create(int userid, string name,
string emailid, char sex, long mob)
{
Console.WriteLine(
"Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create your account\n");
this.userid = 132;
this.name = "Radha";
this.emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com";
this.sex = 'F';
this.mob = 900558981;
Console.WriteLine("your account has been created");
}
}
// This code is contributed by akshatve2zi2
Javascript
class Signup {
constructor(userid, name, emailid, sex, mob) {
this.userid = userid;
this.name = name;
this.emailid = emailid;
this.sex = sex;
this.mob = mob;
}
create(userid, name, emailid, sex, mob) {
console.log("Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create your account\n");
this.userid = 132;
this.name = "Radha";
this.emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com";
this.sex = 'F';
this.mob = 900558981;
console.log("your account has been created");
}
}
console.log("GfG!");
let s1 = new Signup();
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F', 89002);
// This code is contributed by akshatve2zi2
Output
GfG!
Welcome to GeeksforGeeks
Lets create your account
your account has been created
Parallel processing approach(并行处理方法)
Parallel processing is the processing of program instructions by dividing them among multiple processors. A parallel processing system posses many numbers of processor with the objective of running a program in less time by dividing them. This approach seems to be like divide and conquer. Examples are NESL (one of the oldest one) and C/C++ also supports because of some library function.
并行处理是通过将程序指令分配给多个处理器来处理的一种方法。并行处理系统拥有多个处理器,目的是通过分配任务来减少程序的运行时间。这种方法类似于分而治之。例如NESL(最古老的一种),C/C++也支持并行处理,因为它们提供了一些库函数。
Declarative programming paradigm(声明式编程范式)
It is divided as Logic, Functional, Database. In computer science the declarative programming is a style of building programs that expresses logic of computation without talking about its control flow. It often considers programs as theories of some logic.It may simplify writing parallel programs. The focus is on what needs to be done rather how it should be done basically emphasize on what code is actually doing. It just declares the result we want rather how it has be produced. This is the only difference between imperative (how to do) and declarative (what to do) programming paradigms. Getting into deeper we would see logic, functional and database.
声明式编程范式分为逻辑、函数式和数据库三种类型。在计算机科学中,声明式编程是一种构建程序的风格,它表达计算的逻辑,而不涉及其控制流。它通常将程序视为某种逻辑的理论。它可能简化了并行程序的编写。其重点在于需要做什么,而不是如何去做,基本上强调代码的实际作用。它只是声明我们想要的结果,而不是如何产生这个结果。这就是命令式(如何做)和声明式(做什么)编程范式之间的唯一区别。深入探讨后,我们会看到逻辑、函数式和数据库。
Logic programming paradigms(逻辑编程范式)
It can be termed as abstract model of computation. It would solve logical problems like puzzles, series etc. In logic programming we have a knowledge base which we know before and along with the question and knowledge base which is given to machine, it produces result. In normal programming languages, such concept of knowledge base is not available but while using the concept of artificial intelligence, machine learning we have some models like Perception model which is using the same mechanism.
逻辑编程范式可以被视为一种抽象的计算模型。它可以解决逻辑问题,例如谜题、数列等。在逻辑编程中,我们有一个知识库,这是我们事先已知的。除了问题和知识库之外,机器还会产生结果。在普通编程语言中,没有这样的知识库概念,但在使用人工智能、机器学习等概念时,我们有一些模型,例如感知模型,它使用了相同的机制。
In logical programming the main emphasize is on knowledge base and the problem. The execution of the program is very much like proof of mathematical statement, e.g., Prolog
在逻辑编程中,主要强调的是知识库和问题。程序的执行非常类似于数学命题的证明,例如Prolog:
predicates
sumoftwonumber(integer, integer).
clauses
sumoftwonumber(0, 0).
sumoftwonumber(N, R) :-
N > 0,
N1 is N - 1,
sumoftwonumber(N1, R1),
R is R1 + N.
Functional programming paradigms(函数式编程范式)
The functional programming paradigms has its roots in mathematics and it is language independent. The key principle of this paradigms is the execution of series of mathematical functions. The central model for the abstraction is the function which are meant for some specific computation and not the data structure. Data are loosely coupled to functions.The function hide their implementation. Function can be replaced with their values without changing the meaning of the program. Some of the languages like perl, javascript mostly uses this paradigm.
函数式编程范式起源于数学,它是语言无关的。该范式的核心原则是执行一系列数学函数。其抽象的核心模型是函数,用于特定的计算,而不是数据结构。数据与函数松耦合。函数隐藏其实现细节。函数可以用其值替换,而不会改变程序的含义。例如Perl、JavaScript等语言主要使用这种范式。
Examples of Functional programming paradigm:
JavaScript : developed by Brendan Eich
Haskell : developed by Lennart Augustsson, Dave Barton
Scala : developed by Martin Odersky
Erlang : developed by Joe Armstrong, Robert Virding
Lisp : developed by John Mccarthy
ML : developed by Robin Milner
Clojure : developed by Rich Hickey
函数式编程范式示例:
JavaScript:由布兰登·艾奇(Brendan Eich)开发
Haskell:由莱纳特·奥古斯特松(Lennart Augustsson)、戴夫·巴顿(Dave Barton)开发
Scala:由马丁·奥德斯基(Martin Odersky)开发
Erlang:由乔·阿姆斯特朗(Joe Armstrong)、罗伯特·维尔丁(Robert Virding)开发
Lisp:由约翰·麦卡锡(John McCarthy)开发
ML:由罗宾·米尔纳(Robin Milner)开发
Clojure:由里奇·希基(Rich Hickey)开发
Database/Data driven programming approach(数据库/数据驱动编程方法)
This programming methodology is based on data and its movement. Program statements are defined by data rather than hard-coding a series of steps. A database program is the heart of a business information system and provides file creation, data entry, update, query and reporting functions. There are several programming languages that are developed mostly for database application. For example SQL. It is applied to streams of structured data, for filtering, transforming, aggregating (such as computing statistics), or calling other programs. So it has its own wide application.
这种编程方法基于数据及其流动。程序语句由数据定义,而不是硬编码一系列步骤。数据库程序是商业信息系统的核心,提供了文件创建、数据输入、更新、查询和报告功能。有许多编程语言主要是为数据库应用而开发的。例如 SQL。它应用于结构化数据流,用于过滤、转换、聚合(例如计算统计信息)或调用其他程序。因此,它有自己广泛的应用。
CREATE DATABASE databaseAddress;
CREATE TABLE Addr (
PersonID int,
LastName varchar(200),
FirstName varchar(200),
Address varchar(200),
City varchar(200),
State varchar(200)
);