编程范式简介
范式也可以被称为解决问题或完成任务的方法。编程范式是一种使用特定编程语言解决问题的方法。换句话说,它是利用我们可用的工具和技术,按照特定方法解决问题的一种方法论。尽管有许多编程语言,但每种语言通常都遵循一种或多种范式来指导语言的实现。
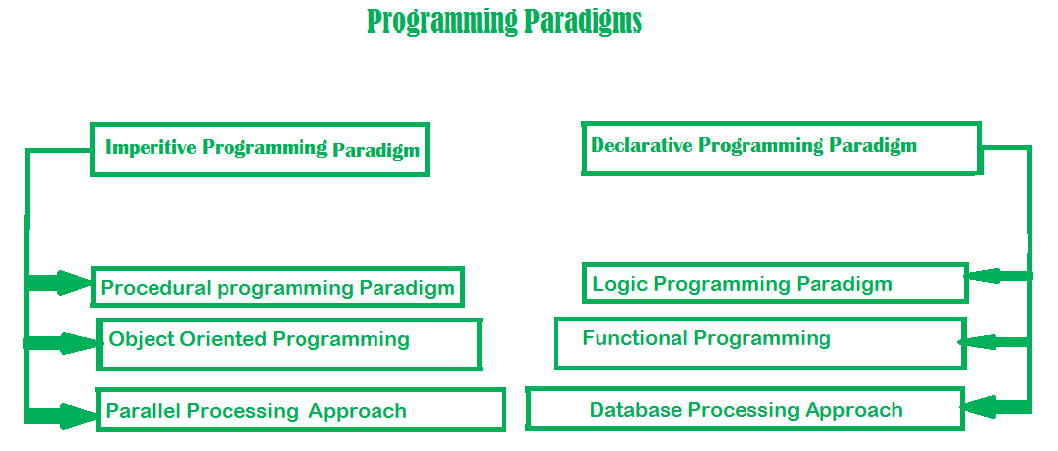
这些方法论或策略被称为编程范式。除了各种编程语言之外,还有几种范式可以解决软件开发中的不同需求和挑战。这些范式如下所述:
命令式编程范式
命令式编程范式是最古老的编程范式之一。它与计算机架构关系密切,基于冯·诺依曼架构。它通过赋值语句改变程序状态来工作,通过逐步改变状态来完成任务。其主要关注点是如何实现目标。该范式由多个语句组成,所有语句执行完毕后将结果存储起来。
优势:
- 实现非常简单
- 包含循环、变量等
劣势:
- 无法解决复杂问题
- 效率较低,生产力不高
- 不支持并行编程
命令式编程范式的示例:
C:由丹尼斯·里奇(Dennis Ritchie)和肯·汤普森(Ken Thompson)开发
Fortran:由约翰·巴库斯(John Backus)为 IBM 开发
Basic:由约翰·G·基门尼(John G. Kemeny)和托马斯·E·库尔茨(Thomas E. Kurtz)开发
C++
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// Array to store marks
int marks[5] = { 12, 32, 45, 13, 19 };
// Variable to store the sum of marks
int sum = 0;
// Variable to store the average
float average = 0.0;
// Calculate the sum of marks
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum = sum + marks[i];
}
// Calculate the average
average = sum / 5.0;
// Output the average
std::cout << "Average of five numbers: " << average << std::endl;
return 0;
}
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// Array to store marks
int marks[5] = { 12, 32, 45, 13, 19 };
// Variable to store the sum of marks
int sum = 0;
// Variable to store the average
float average = 0.0;
// Calculate the sum of marks
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum = sum + marks[i];
}
// Calculate the average
average = (float)sum / 5.0;
// Output the average
printf("Average of five numbers: %.2f\n", average);
return 0;
}
Java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Array to store marks
int[] marks = {12, 32, 45, 13, 19};
// Variable to store the sum of marks
int sum = 0;
// Variable to store the average
float average = 0.0f;
// Calculate the sum of marks
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum = sum + marks[i];
}
// Calculate the average
average = sum / 5.0f;
// Output the average
System.out.println("Average of five numbers: " + average);
}
}
Python
def main():
# Array to store marks
marks = [12, 32, 45, 13, 19]
# Variable to store the sum of marks
total_marks = sum(marks)
# Calculate the average
average = total_marks / len(marks)
# Output the average
print("Average of five numbers:", average)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
#this code is added by Utkarsh
JavaScript
// Array to store marks
let marks = [12, 32, 45, 13, 19];
// Variable to store the sum of marks
let sum = 0;
// Variable to store the average
let average = 0.0;
// Calculate the sum of marks
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum = sum + marks[i];
}
// Calculate the average
average = sum / 5.0;
// Output the average
console.log("Average of five numbers: " + average);
Output
Average of five numbers: 24.2
命令式编程分为三大类:过程式、面向对象和并行处理。这些范式如下所述:
过程式编程范式
该范式强调过程,即底层机器模型。过程式编程与命令式编程没有区别。它能够重用代码,当时它被使用时,由于其可重用性,它是一个巨大的优势。
过程式编程范式的示例:
C:由丹尼斯·里奇(Dennis Ritchie)和肯·汤普森(Ken Thompson)开发
C++:由比雅尼·斯特劳斯特鲁普(Bjarne Stroustrup)开发
Java:由詹姆斯·高斯林(James Gosling)在Sun Microsystems开发
ColdFusion:由J. J. Allaire开发
Pascal:由尼克劳斯·维尔特(Niklaus Wirth)开发
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i, fact = 1, num;
cout << "Enter any Number: ";
cin >> number;
for (i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact = fact * i;
}
cout << "Factorial of " << num << " is: " << fact << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Scanner object for reading input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Prompt user to enter a number
System.out.println("Enter any Number: ");
// Read number from user input
int num = scanner.nextInt();
// Initialize factorial to 1
int fact = 1;
// Calculate factorial using a for loop
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact = fact * i;
}
// Print the factorial of the number
System.out.println("Factorial of " + num + " is: " + fact);
}
}
Python
# Prompt user to enter a number
num = int(input("Enter any Number: "))
fact = 1 # Initialize factorial variable
# Calculate factorial
for i in range(1, num + 1):
fact = fact * i
# Print the factorial
print("Factorial of", num, "is:", fact)
Javascript
// Prompt the user for input
let num = prompt("Enter any Number: ");
// Initialize the factorial value to 1
let fact = 1;
// Calculate the factorial of the number
for (let i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact = fact * i;
}
// Print the factorial of the number
console.log("Factorial of " + num + " is: " + fact);
面向对象编程范式
程序被编写成一系列类和对象的集合,这些类和对象用于通信。最基本的实体是对象,所有计算都在对象上进行。更强调数据而不是过程。它可以处理几乎所有当前场景中的现实问题。
优势:
- 数据安全性
- 继承
- 代码可重用性
- 灵活且具有抽象性
面向对象编程范式的示例:
Simula:第一种面向对象的编程语言
Java:由詹姆斯·高斯林(James Gosling)在Sun Microsystems开发
C++:由比雅尼·斯特劳斯特鲁普(Bjarne Stroustrup)开发
Objective-C:由布拉德·考克斯(Brad Cox)设计
Visual Basic .NET:由微软开发
Python:由吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum)开发
Ruby:由松本行弘(Yukihiro Matsumoto)开发
Smalltalk:由艾伦·凯(Alan Kay)、丹·英格尔斯(Dan Ingalls)和阿德莱·戈德堡(Adele Goldberg)开发
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Class Signup
class Signup {
int userid;
string name;
string emailid;
char sex;
long mob;
public:
// Function to create and object using
// the parameters
void create(int userid, string name, string emailid,
char sex, long mob)
{
cout << "Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create "
"your account\n";
this->userid = 132;
this->name = "Radha";
this->emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com";
this->sex = 'F';
this->mob = 900558981;
cout << "your account has been created" << endl;
}
};
// Driver Cpde
int main()
{
cout << "GfG!" << endl;
// Creating Objects
Signup s1;
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F', 89002);
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("GfG!");
Signup s1 = new Signup();
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F',
89002);
}
}
class Signup {
int userid;
String name;
String emailid;
char sex;
long mob;
public void create(int userid, String name,
String emailid, char sex, long mob)
{
System.out.println(
"Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create your account\n");
this.userid = 132;
this.name = "Radha";
this.emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com";
this.sex = 'F';
this.mob = 900558981;
System.out.println("your account has been created");
}
}
Python
class Signup:
def __init__(self):
self.userid = 0
self.name = ""
self.emailid = ""
self.sex = ""
self.mob = 0
def create(self, userid, name, emailid, sex, mob):
print("Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create your account\n")
self.userid = 132
self.name = "Radha"
self.emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com"
self.sex = 'F'
self.mob = 900558981
print("your account has been created")
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("GfG!")
s1 = Signup()
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F', 89002)
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("GfG!");
Signup s1 = new Signup();
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F',
89002);
}
}
class Signup {
public int userid;
public string name;
public string emailid;
public char sex;
public long mob;
public void create(int userid, string name,
string emailid, char sex, long mob)
{
Console.WriteLine(
"Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create your account\n");
this.userid = 132;
this.name = "Radha";
this.emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com";
this.sex = 'F';
this.mob = 900558981;
Console.WriteLine("your account has been created");
}
}
// This code is contributed by akshatve2zi2
Javascript
class Signup {
constructor(userid, name, emailid, sex, mob) {
this.userid = userid;
this.name = name;
this.emailid = emailid;
this.sex = sex;
this.mob = mob;
}
create(userid, name, emailid, sex, mob) {
console.log("Welcome to GeeksforGeeks\nLets create your account\n");
this.userid = 132;
this.name = "Radha";
this.emailid = "radha.89@gmail.com";
this.sex = 'F';
this.mob = 900558981;
console.log("your account has been created");
}
}
console.log("GfG!");
let s1 = new Signup();
s1.create(22, "riya", "riya2@gmail.com", 'F', 89002);
// This code is contributed by akshatve2zi2
Output
GfG!
Welcome to GeeksforGeeks
Lets create your account
your account has been created
并行处理方法
并行处理是通过将程序指令分配给多个处理器来处理的一种方法。并行处理系统拥有多个处理器,目的是通过分配任务来减少程序的运行时间。这种方法类似于分而治之。例如 NESL(最古老的一种),C/C++也支持并行处理,因为它们提供了一些库函数。
声明式编程范式
声明式编程范式分为逻辑、函数式和数据库三种类型。在计算机科学中,声明式编程是一种构建程序的风格,它表达计算的逻辑,而不涉及其控制流。它通常将程序视为某种逻辑的理论。它可能简化了并行程序的编写。其重点在于需要做什么,而不是如何去做,基本上强调代码的实际作用。它只是声明我们想要的结果,而不是如何产生这个结果。这就是命令式(如何做)和声明式(做什么)编程范式之间的唯一区别。深入探讨后,我们会看到逻辑、函数式和数据库。
逻辑编程范式
逻辑编程范式可以被视为一种抽象的计算模型。它可以解决逻辑问题,例如谜题、数列等。在逻辑编程中,我们有一个知识库,这是我们事先已知的。除了问题和知识库之外,机器还会产生结果。在普通编程语言中,没有这样的知识库概念,但在使用人工智能、机器学习等概念时,我们有一些模型,例如感知模型,它使用了相同的机制。
在逻辑编程中,主要强调的是知识库和问题。程序的执行非常类似于数学命题的证明,例如
Prolog:
predicates
sumoftwonumber(integer, integer).
clauses
sumoftwonumber(0, 0).
sumoftwonumber(N, R) :-
N > 0,
N1 is N - 1,
sumoftwonumber(N1, R1),
R is R1 + N.
函数式编程范式
函数式编程范式起源于数学,它是语言无关的。该范式的核心原则是执行一系列数学函数。其抽象的核心模型是函数,用于特定的计算,而不是数据结构。数据与函数松耦合。函数隐藏其实现细节。函数可以用其值替换,而不会改变程序的含义。例如 Perl、JavaScript 等语言主要使用这种范式。
函数式编程范式示例:
JavaScript:由布兰登·艾奇(Brendan Eich)开发
Haskell:由莱纳特·奥古斯特松(Lennart Augustsson)、戴夫·巴顿(Dave Barton)开发
Scala:由马丁·奥德斯基(Martin Odersky)开发
Erlang:由乔·阿姆斯特朗(Joe Armstrong)、罗伯特·维尔丁(Robert Virding)开发
Lisp:由约翰·麦卡锡(John McCarthy)开发
ML:由罗宾·米尔纳(Robin Milner)开发
Clojure:由里奇·希基(Rich Hickey)开发
数据库/数据驱动编程方法
这种编程方法基于数据及其流动。程序语句由数据定义,而不是硬编码一系列步骤。数据库程序是商业信息系统的核心,提供了文件创建、数据输入、更新、查询和报告功能。有许多编程语言主要是为数据库应用而开发的。例如 SQL。它应用于结构化数据流,用于过滤、转换、聚合(例如计算统计信息)或调用其他程序。因此,它有自己广泛的应用。
CREATE DATABASE databaseAddress;
CREATE TABLE Addr (
PersonID int,
LastName varchar(200),
FirstName varchar(200),
Address varchar(200),
City varchar(200),
State varchar(200)
);
备注:文章翻译自Introduction of Programming Paradigms - GeeksforGeeks